Interpreter vs Compiler#
High level language#
A high-level language is one that is understandable by us, humans. This is called source code.
Machine code#
Computers do not understand high-level language. It only understands the program written in 0’s and 1’s in binary, called the machine code.
To convert source code into machine code, we use either a compiler or an interpreter.
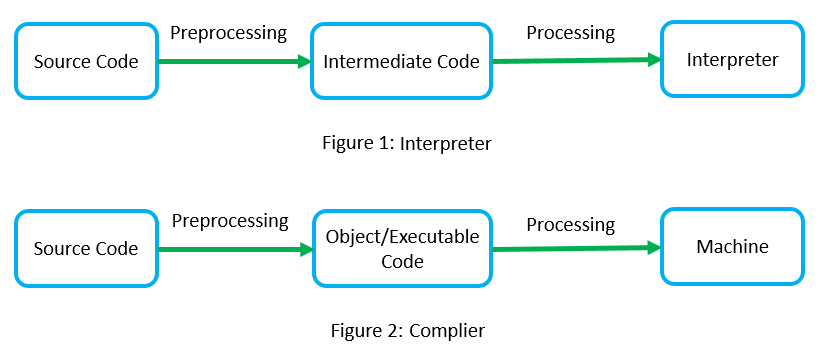
Interpreter#
A computer program, which converts each high-level program statement into the machine code. This includes source code, pre-compiled code, and scripts.
Interpreters convert code into machine code when the program is run.
Compiler#
A compiler is a computer program that transforms code written in a high-level programming language into the machine code.
A compiler will convert the code into machine code (create an exe) before program run.
Programming Steps Comparision:#
# |
Interpreter |
Compiler |
|---|---|---|
1. |
Create the Program. |
Create the program. |
2. |
No linking of files or machine code generation. |
Compile will parse or analyses all of the language statements for its correctness. If incorrect, throws an error. |
3. |
Source statements executed line by line DURING Execution. |
If no error, the compiler will convert source code to machine code. |
4. |
- |
It links different code files into a runnable program(know as exe). |
5. |
- |
Run the Program |
Parameters |
Interpreter |
Compiler |
|---|---|---|
Advantage |
Interpreters are easier to use, especially for beginners. |
The program code is already translated into machine code. Thus, it code execution time is less. |
Disadvantage |
Interpreted programs can run on computers that have the corresponding interpreter. |
You can’t change the program without going back to the source code. |
Machine code |
Not saving machine code at all. |
Store machine language as machine code on the disk. |
Running time |
Interpreters usually take less amount of time to analyze the source code. However, the overall execution time is comparatively slower than compilers. |
Compilers usually take a large amount of time to analyze the source code. However, the overall execution time is comparatively faster than interpreters. |
Model |
It is based on interpretation method. |
It is based on language translation linking-loading model. |
Program generation |
Do not generate output program. So they evaluate the source program at every time during execution. |
Generates output program (in the form of .exe) which can be run independently from the original program. |
Execution |
It does not convert source code into machine code instead it scans it line by line. |
It converts the source code into machine code. |
Memory requirement |
No Object Code is generated, hence are memory efficient. |
Generates Object Code which further requires linking, hence requires more memory. |
Best suited for |
For web environments, where load times are important. Due to all the exhaustive analysis is done, compiles take relatively larger time to compile even small code that may not be run multiple times. In such cases, interpreters are better. |
Bounded to the specific target machine and cannot be ported. C and C++ are a most popular a programming language which uses compilation model. |
Code Optimization |
Interpreters see code line by line, and thus optimizations are not as robust as compilers. |
The compiler sees the entire code upfront. Hence, they perform lots of optimizations that make code run faster. |
Dynamic Typing |
Interpreted languages support Dynamic Typing |
Difficult to implement as compilers cannot predict what happens at turn time. |
Usage |
It is best suited for the program and development environment. |
It is best suited for the production environment. |
Error execution |
The interpreter reads a single statement and shows the error if any. You must correct the error to interpret next line. |
Compiler displays all errors and warning at the compilation time. Therefore, you can’t run the program without fixing errors. |
Input |
It takes a single line of code. |
It takes an entire program. |
Output |
Interpreter never generate any intermediate machine code. |
Compliers generates intermediate machine code. |
Errors |
Considering it scans code one line at a time, errors are shown line by line. |
As it scans the code in one go, the errors (if any) are shown at the end together. |
Programming languages |
JavaScript, MATLAB, Python, Ruby, PHP, Pearl use interpreters. |
C, C++, C#, Java use compilers. |


