Introduction#
Python is a popular and easy-to-learn programming language. Whether you’re new to coding or looking to expand your skills, Python is a great place to start.
✨ What Can Python Do?#
🌐 Web Development: Create web applications on a server.
🔄 Automation: Build workflows and automate tasks.
🗄️ Data Handling: Connect to databases, read, and modify files.
📊 Big Data & Math: Handle big data and perform complex calculations.
⚙️ Prototyping: Quickly create prototypes or production-ready software.
🤖 Machine Learning: Develop, train, and deploy machine learning models.
…and a lot more!
💡 Why Choose Python?#
💻 Cross-Platform: Works on various platforms (Windows, Mac, Linux, Raspberry Pi).
📝 Easy Syntax: Simple syntax that resembles the English language.
⏱️ Efficient Coding: Write programs with fewer lines of code.
🚀 Quick Prototyping: Runs on an interpreter, allowing immediate code execution.
🧠 Versatility: Supports multiple programming styles: procedural, object-oriented, or functional.
📚 How Python Runs a Program#
1. Writing the Code 📝#
Write your Python code in a .py file. This code is written in a human-readable format, using Python’s easy-to-understand syntax.
2. The Python Interpreter 🐍#
Upon execution, the Python interpreter comes into play. The interpreter is like a translator that reads your Python code and converts it into something the computer can understand.
3. Lexical Analysis 🔍#
The interpreter first performs lexical analysis. It breaks your code down into tokens (like keywords, variables, operators, etc.). It’s like breaking a sentence into words and punctuation.
4. Parsing 📚#
Next, the interpreter checks if your code follows Python’s rules (syntax). This step creates a parse tree or an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST), which organizes the tokens into a structure that makes sense.
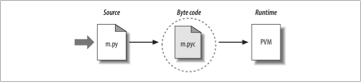
5. Bytecode Compilation ⚙️#
The AST is then converted into bytecode. Bytecode is a lower-level representation of your code. This bytecode is what Python actually executes.
6. Python Virtual Machine (PVM) 🖥️#
The bytecode is sent to the Python Virtual Machine (PVM), which is a part of the Python interpreter. The PVM reads the bytecode and performs the instructions, which makes the program run.
Modules#
Get started by installing Python on your system.
Learn the fundamentals of Python’s syntax and symantics.
Dive into functions and modular programming in Python.
Learn about object-oriented programming in Python.
Learn about exception handling in Python.
Learn how to handle files in Python.
Learn about datetime operations in Python.
Delve into advanced Python topics for seasoned developers.
Compare interpreters and compilers in the context of Python.
Test your knowledge with practical Python exercises.
