DeepSeek-V3: A Technical Overview of a Novel Mixture-of-Experts Model#
DeepSeek-V3 emerges as a significant advancement in the field of large language models (LLMs). This model, detailed in the accompanying technical report, employs a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, a design choice that allows for both high performance and computational efficiency. The architecture is composed of a number of expert sub-networks, which are activated conditionally based on the input, enabling the model to scale effectively. The training process involved a large corpus of text and code data, leveraging a combination of supervised learning and reinforcement learning techniques. DeepSeek-V3 demonstrates strong performance across a range of benchmarks, while maintaining a focus on efficient inference. The model is available on GitHub, providing access to both the model weights and the technical documentation.
Architectural Innovations and Training Efficiency#
DeepSeek-V3 builds upon the efficient architecture of DeepSeek-V2, incorporating several key innovations to enhance performance and training efficiency. The model utilizes a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with 671 billion total parameters, of which 37 billion are activated for each token. This design allows for a large model capacity while maintaining computational efficiency during inference.
A core component of DeepSeek-V3 is the Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) mechanism. This attention mechanism, thoroughly validated in DeepSeek-V2, contributes to the model’s ability to process information effectively. The DeepSeekMoE architecture, also inherited from DeepSeek-V2, further optimizes the model’s performance by enabling efficient routing of tokens to different experts.
A significant innovation in DeepSeek-V3 is the introduction of an auxiliary-loss-free strategy for load balancing. Traditional load balancing techniques often involve auxiliary losses that can negatively impact model performance. DeepSeek-V3’s approach mitigates this issue by achieving effective load balancing without the performance degradation associated with auxiliary losses. This is a crucial step toward optimizing the MoE architecture for maximum efficiency.
Furthermore, DeepSeek-V3 employs a Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) objective during training. This objective has been shown to improve model performance and can also be used for speculative decoding, potentially accelerating inference.
The pre-training of DeepSeek-V3 leverages an FP8 mixed precision training framework. This is the first validation of FP8 training on an extremely large-scale model, demonstrating its feasibility and effectiveness. The use of FP8 significantly reduces memory requirements and computational costs, enabling the training of larger models with fewer resources.
To overcome communication bottlenecks in cross-node MoE training, DeepSeek-V3 employs a co-design approach involving algorithms, frameworks, and hardware. This approach achieves near full computation-communication overlap, significantly improving training efficiency and reducing training costs. This allows for scaling up the model size without incurring additional overhead.
The pre-training of DeepSeek-V3 was completed on 14.8 trillion tokens using only 2.664 million H800 GPU hours. This cost-effective training process resulted in a strong open-source base model. The subsequent fine-tuning stages required only 0.1 million GPU hours, further highlighting the efficiency of the training process.
The model’s architecture and training methodology are designed for stability. Throughout the entire training process, no irrecoverable loss spikes or rollbacks were experienced.
cd inference
python fp8_cast_bf16.py --input-fp8-hf-path /path/to/fp8_weights --output-bf16-hf-path /path/to/bf16_weights
The provided code snippet demonstrates how to convert FP8 weights to BF16, which is useful for experimentation.
Post-Training and Performance Benchmarks#
Post-Training: Knowledge Distillation from DeepSeek-R1#
We employ an innovative methodology to distill reasoning capabilities from a long-Chain-of-Thought (CoT) model, specifically from one of the DeepSeek R1 series models, into standard Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly DeepSeek-V3. Our pipeline incorporates the verification and reflection patterns of R1 into DeepSeek-V3, which notably improves its reasoning performance. Furthermore, we maintain control over the output style and length of DeepSeek-V3.
Performance Benchmarks#
DeepSeek-V3 demonstrates strong performance across a range of benchmarks, as detailed below.
Base Model Performance#
The following table compares DeepSeek-V3’s base model performance against other models on standard benchmarks:
DeepSeek-V3 achieves the best performance on most benchmarks, particularly on math and code tasks.
Context Window Evaluation#
The Needle In A Haystack (NIAH) test results indicate that DeepSeek-V3 maintains strong performance across all context window lengths up to 128K.
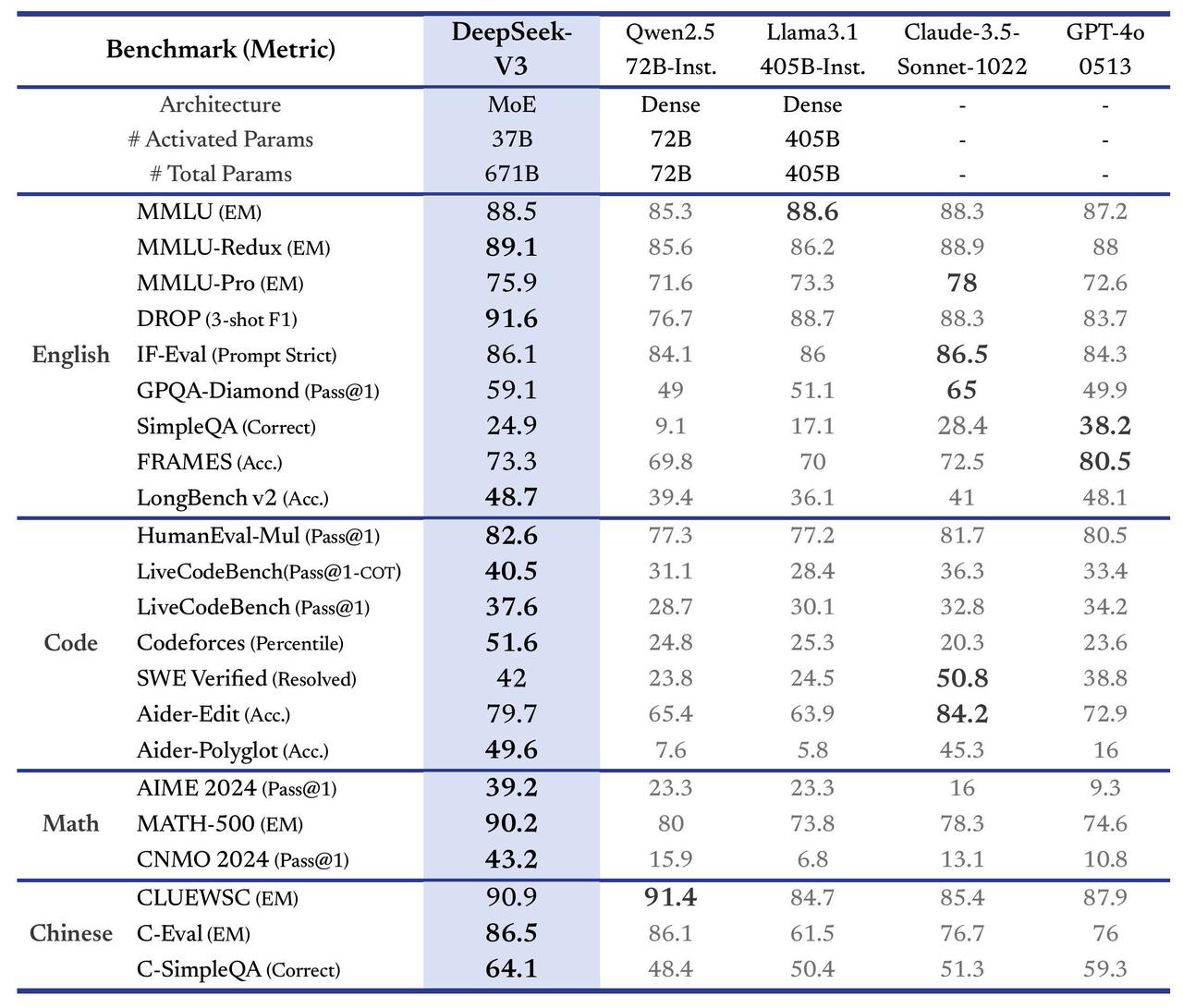
Chat Model Performance#
The following table compares DeepSeek-V3’s chat model performance against other models (larger than 67B) on standard benchmarks:
DeepSeek-V3 stands as the best-performing open-source model and exhibits competitive performance against frontier closed-source models.
Open-Ended Generation Evaluation#
Model |
Arena-Hard |
AlpacaEval 2.0 |
|---|---|---|
DeepSeek-V2.5-0905 |
76.2 |
50.5 |
Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct |
81.2 |
49.1 |
LLaMA-3.1 405B |
69.3 |
40.5 |
GPT-4o-0513 |
80.4 |
51.1 |
Claude-Sonnet-3.5-1022 |
85.2 |
52.0 |
DeepSeek-V3 |
85.5 |
70.0 |
DeepSeek-V3 achieves the top scores in both Arena-Hard and AlpacaEval 2.0 for English open-ended conversation.
Model Availability and Local Deployment#
DeepSeek-V3 models are available for download on Hugging Face, with two variants: DeepSeek-V3-Base and DeepSeek-V3. The total size of the models on Hugging Face is 685B, which includes 671B for the main model weights and 14B for the Multi-Token Prediction (MTP) module weights.
To facilitate local deployment, DeepSeek-V3 supports multiple hardware and open-source community software options:
DeepSeek-Infer Demo: A lightweight demo is provided for FP8 and BF16 inference. This serves as a basic example for running the model.
SGLang: SGLang fully supports DeepSeek-V3 with both BF16 and FP8 inference modes. It leverages Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) optimizations, FP8 (W8A8), FP8 KV Cache, and Torch Compile for efficient performance on both NVIDIA and AMD GPUs.
LMDeploy: This framework enables efficient FP8 and BF16 inference for local and cloud deployment. It integrates with PyTorch-based workflows and offers offline and online deployment capabilities.
TensorRT-LLM: TensorRT-LLM supports BF16 inference and INT4/8 quantization for DeepSeek-V3, with FP8 support planned for the near future. A custom branch is available for direct experience with these features.
vLLM: vLLM supports DeepSeek-V3 with FP8 and BF16 modes, utilizing tensor parallelism and pipeline parallelism for distributed inference.
AMD GPU: DeepSeek-V3 can be run on AMD GPUs using SGLang, with full compatibility for both BF16 and FP8 precision.
Huawei Ascend NPU: The MindIE framework supports running the BF16 version of DeepSeek-V3 on Huawei Ascend devices.
Since FP8 training is natively adopted in the DeepSeek-V3 framework, only FP8 weights are provided. For users requiring BF16 weights for experimentation, a conversion script is available:
cd inference
python fp8_cast_bf16.py --input-fp8-hf-path /path/to/fp8_weights --output-bf16-hf-path /path/to/bf16_weights
It is important to note that Hugging Face’s Transformers library does not currently have direct support for DeepSeek-V3.
For detailed instructions on running DeepSeek-V3 with each of these options, please refer to the links provided in the original document.
Conclusion#
In summary, DeepSeek-V3 represents a significant advancement in large language model technology, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a range of benchmarks while maintaining remarkable efficiency. Its optimized architecture and training methodologies have resulted in a model that is both powerful and practical for real-world applications. We encourage researchers and developers to explore the model’s capabilities, delve into the technical details outlined in the provided resources, and leverage DeepSeek-V3 to push the boundaries of what’s possible with AI. Access the model and its associated resources on the official GitHub repository: deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3 and the technical report: deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3.


Comments
comments powered by Disqus